The following code is for data retrieval through the LPT port using Delphi 7 and components of the program interface inpout32.dll LPT. Download inpout32.dll and saved in the same folder with the exe application
unit Unit1;
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms,
Dialogs, StdCtrls;
function Inp32(PortAdr: word): byte; stdcall; external 'inpout32.dll';
function Out32(PortAdr: word; Data: byte): byte; stdcall; external 'inpout32.dll';
type
TForm1 = class(TForm)
Edit1: TEdit;
Button1: TButton;
Button2: TButton;
Label1: TLabel;
Label2: TLabel;
Edit2: TEdit;
Label3: TLabel;
Edit3: TEdit;
procedure Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure Button2Click(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
Form1: TForm1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
procedure TForm1.Button1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
Port: word;
Data: Byte;
begin
Data:= StrToInt(Edit1.Text);
Port:= StrToInt(Edit2.Text);
Out32(Port, Data);
end;
procedure TForm1.Button2Click(Sender: TObject);
var
Port: word;
Data: Byte;
begin
Port:= StrToInt(Edit3.Text);
Data:= Inp32(Port);
MessageDlg('Value: '+ IntToStr(Data), mtInformation, [mbOK], 0);
end;
end.
download complete Delphi 7 code
.:: eLiNTS ::.
Electrical, Instrumentation and Programming
Monday, August 30, 2010
Wednesday, August 25, 2010
Difference between RS232 & RS485
| SPECIFICATIONS | RS232 | RS423 | RS422 | RS485 |
| Mode of Operation | SINGLE -ENDED | SINGLE -ENDED | DIFFERENTIAL | DIFFERENTIAL |
| Total Number of Drivers and Receivers on One Line (One driver active at a time for RS485 networks) | 1 DRIVER 1 RECVR | 1 DRIVER 10 RECVR | 1 DRIVER 10 RECVR | 32 DRIVER 32 RECVR |
| Maximum Cable Length | 50 FT. | 4000 FT. | 4000 FT. | 4000 FT. |
| Maximum Data Rate (40ft. - 4000ft. for RS422/RS485) | 20kb/s | 100kb/s | 10Mb/s-100Kb/s | 10Mb/s-100Kb/s |
| Maximum Driver Output Voltage | +/-25V | +/-6V | -0.25V to +6V | -7V to +12V |
| Driver Output Signal Level (Loaded Min.) | +/-5V to +/-15V | +/-3.6V | +/-2.0V | +/-1.5V |
| Driver Output Signal Level (Unloaded Max) | +/-25V | +/-6V | +/-6V | +/-6V |
| Driver Load Impedance (Ohms) | 3k to 7k | >=450 | 100 | 54 |
| Max. Driver Current in High Z State (Power ON) | N/A | N/A | N/A | +/-100uA |
| Max. Driver Current in High Z State (Power OFF) | +/-6mA @ +/-2v | +/-100uA | +/-100uA | +/-100uA |
| Slew Rate (Max.) | 30V/uS | Adjustable | N/A | N/A |
| Receiver Input Voltage Range | +/-15V | +/-12V | -10V to +10V | -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Input Sensitivity | +/-3V | +/-200mV | +/-200mV | +/-200mV |
| Receiver Input Resistance (Ohms), (1 Standard Load for RS485) | 3k to 7k | 4k min. | 4k min. | 12k |
Serial RS485
RS-485 standard supports half-duplex data communication, this means that in order to send and receive data using only two cable channels. The specifications of this standard can support data communications from a number of devices and is also capable of supporting data communication in a distance up to 1200 meters. Connection from each device connected to the RS-485 carried out in parallel, so that connection and release device can be done without disrupting the whole network work.
To adjust the impedance of the cable used to install a resistor whose value is adjusted with the characteristic impedance of the cable (~ 120 Ohm). Communication network topology using the RS-485 data can be viewed at the following picture.
 Here datasheet for RS485
Here datasheet for RS485
To adjust the impedance of the cable used to install a resistor whose value is adjusted with the characteristic impedance of the cable (~ 120 Ohm). Communication network topology using the RS-485 data can be viewed at the following picture.
 Here datasheet for RS485
Here datasheet for RS485Serial RS232
Serial Ports come in two "sizes", There are the D25 pin type connector and the D9 pin type connector, both of which are male on the back of the PC, thus you will require a female connector on your device. Below is a table of pin connections for the 9 pin and 25 pin D-Type connectors.

Null Modems
A Null Modem is used to connect two serial communication devices. This is commonly used as a cheap way to network games or to transfer files between computers (using Zmodem Protocol, Xmodem Protocol etc). This can also be used with many Microprocessor Development Systems. It only requires 3 wires (TD, RD & SG) to be wired straight through thus is more cost effective to use with long cable runs.
 LoopBack
LoopBack
It has the receive and transmit lines connected together, so that anything transmitted out of the Serial Port is immediately received by the same port. If you connect this to a Serial Port an load a Terminal Program, anything you type will be immediately displayed on the screen.
 Here datasheet for RS232
Here datasheet for RS232

| DB9 | DB25 | Abbrevation | Function |
| 1 | 8 | CD | Carrier Detect |
| 2 | 3 | RD | Receive Data |
| 3 | 2 | TD | Transmit Data |
| 4 | 20 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 5 | 7 | SG | Signal Ground |
| 6 | 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready |
| 7 | 4 | RTS | Request To Send |
| 8 | 5 | CTS | Clear To Send |
| 9 | 22 | RI | Ring Indicator |
| Abbrevation | Function | Description |
| CD | Carrier Detect | When the modem detects a "Carrier" from the modem at the other end of the phone line, this Line becomes active. |
| RD | Receive Data | Serial Data Input (RXD) |
| TD | Transmit Data | Serial Data Output (TXD) |
| DTR | Data Terminal Ready | This is the opposite to DSR. This tells the Modem that the UART is ready to link. |
| DSR | Data Set Ready | This tells the UART that the modem is ready to establish a link. |
| RTS | Request To Send | This line informs the Modem that the UART is ready to exchange data. |
| CTS | Clear To Send | This line indicates that the Modem is ready to exchange data. |
| RI | Ring Indicator | Goes active when modem detects a ringing signal from the PSTN. |
Null Modems
A Null Modem is used to connect two serial communication devices. This is commonly used as a cheap way to network games or to transfer files between computers (using Zmodem Protocol, Xmodem Protocol etc). This can also be used with many Microprocessor Development Systems. It only requires 3 wires (TD, RD & SG) to be wired straight through thus is more cost effective to use with long cable runs.
 LoopBack
LoopBackIt has the receive and transmit lines connected together, so that anything transmitted out of the Serial Port is immediately received by the same port. If you connect this to a Serial Port an load a Terminal Program, anything you type will be immediately displayed on the screen.
 Here datasheet for RS232
Here datasheet for RS232Serial Port Overview
The Serial Port is harder to interface than the Parallel Port. In most cases, any device you connect to the serial port will need the serial transmission converted back to parallel so that it can be used directly. This can be done using a UART. On the software side of things, there are many more registers that you have to attend to than on a Standard Parallel Port.
So what are the advantages of using serial data transfer rather than parallel ?
So what are the advantages of using serial data transfer rather than parallel ?
- Serial Cables can be longer than Parallel cables. The serial port transmits a '1' as -3 to -25 volts and a '0' as +3 to +25 volts where as a parallel port transmits a '0' as 0v and a '1' as 5v. Therefore the serial port can have a maximum swing of 50V compared to the parallel
port which has a maximum swing of 5 Volts. Therefore cable loss is not going to be as much of a problem for serial cables than they are for parallel. - You don't need as many wires than parallel transmission. If your device needs to be mounted a far distance away from the computer then 3 core cable (Null Modem Configuration) is going to be a lot cheaper than running 19 or 25 core cable for paralel device.
- Microcontroller's have also proven to be quite popular recently. Many of these have in built SCI (Serial Communications Interfaces) which can be used to talk to the outside world. Serial Communication reduces the pin count of these MPU's. Only two pins are commonly used, Transmit Data (TXD) and Receive Data (RXD) compared with at least 8 pins if you use a 8 bit Parallel method (You may also require a Strobe).
Tuesday, August 24, 2010
LPT Port
Parallel port is a simple and inexpensive tool for building computer controlled devices and projects. The simplicity and ease of programming makes parallel port popular in electronics hobbyist world. The parallel port is often used in Computer controlled robots, Atmel/PIC programmers, home automation, ...etc. Here a simple tutorial on parallel port interfacing and programming with some examples.
You can see the parallel port connector in the rear panel of your PC. It is a 25 pin female (DB25) connector (to which printer is connected). On almost all the PCs only one parallel port is present, but you can add more by inserting ISA/PCI parallel port cards.
The pin outs of DB25 connector is shown in the picture below
The pin outs of DB25 connector is shown in the picture below
The lines in DB25 connector are divided in to three groups, they are
1. Data bus
2. Control bus
3. Status bus
The details of parallel port signal lines are given below
Register Address
The details of parallel port signal lines are given below
| Pin Number | Signal name | Direction | Register Bit | Inverted |
| 1 | nStrobe | Out | Control-0 | Yes |
| 2 | Data0 | In/Out | Data-0 | No |
| 3 | Data1 | In/Out | Data-1 | No |
| 4 | Data2 | In/Out | Data-2 | No |
| 5 | Data3 | In/Out | Data-3 | No |
| 6 | Data4 | In/Out | Data-4 | No |
| 7 | Data5 | In/Out | Data-5 | No |
| 8 | Data6 | In/Out | Data-6 | No |
| 9 | Data7 | In/Out | Data-7 | No |
| 10 | nAck | In | Status-6 | No |
| 11 | Busy | In | Status-7 | Yes |
| 12 | Paper-Out | In | Status-5 | No |
| 13 | Select | In | Status-4 | No |
| 14 | Linefeed | Out | Control-1 | Yes |
| 15 | nError | In | Status-3 | No |
| 16 | nInitialize | Out | Control-2 | No |
| 17 | nSelect-Printer | Out | Control-3 | Yes |
| 18-25 | Ground | - | - | - |
Register Address
| Register | LPT1 | LPT2 |
| data registar(baseaddress + 0) | 0x378 | 0x278 |
| status register (baseaddress + 1) | 0x379 | 0x279 |
| control register (baseaddress + 2) | 0x37a | 0x27a |
Saturday, August 21, 2010
Backpropagation Algorithm
Backpropagation algorithm was first formulated by Werbos and popularized by Rumelhart and Mc. Clelland to wear on ANN (Artificial Neural Nets), and is commonly abbreviated algorithm with BP. These algorithms include supervised learning method and designed for operation on the feed forward multi-layer nets.
Backpropagation method is used widely. An estimated 90% is used in many fields, among others in the financial sector, handwriting pattern recognition, and the introduction of sound and color.
This algorithm is widely used in applications settings because the learning process is based on a simple relationship, ie, if the output gives the wrong result, the weight is corrected so that errors can be reduced and the net response is expected to be closer to the true price. Backpropagation is also capable to handle weight in the hidden layer (hidden).
Broadly speaking this algorithm describes, when the nets are given input patterns as training patterns so that pattern to the nodes in the hidden layer to be forwarded to the output layer nodes. Then the output layer nodes is called the output response of the net. When the net output is not equal to the expected output then the output will be spread back on the hidden layer forwarded to the node in the input layer. Therefore, the mechanism is called the backpropagation training.
Training Phase
Backpropagation method is used widely. An estimated 90% is used in many fields, among others in the financial sector, handwriting pattern recognition, and the introduction of sound and color.
This algorithm is widely used in applications settings because the learning process is based on a simple relationship, ie, if the output gives the wrong result, the weight is corrected so that errors can be reduced and the net response is expected to be closer to the true price. Backpropagation is also capable to handle weight in the hidden layer (hidden).
Broadly speaking this algorithm describes, when the nets are given input patterns as training patterns so that pattern to the nodes in the hidden layer to be forwarded to the output layer nodes. Then the output layer nodes is called the output response of the net. When the net output is not equal to the expected output then the output will be spread back on the hidden layer forwarded to the node in the input layer. Therefore, the mechanism is called the backpropagation training.
Training Phase
This training phase is the step how a neural net was trained, that is by making changes the connection weights. While the phase of problem solving will be done if the learning process is completed, phase is the process of testing or testing.
Backpropagation algorithm consists of two processes, namely the feed forward and backpropagation of error. To more clearly be described as follows :
1. Initialize weight factors with small random values.
2. Repeat steps 2 through 9 until the stop condition is met.
3. Perform steps 3 through 8 for each pair of training.
4. Each input unit (Xi, i = 1, ... n) receives input signals Xi and the signals are distributed to the upper unit of the hidden layer (hidden units).
5. Each hidden summing weighted factors :
 and counted in accordance with the activation function:
and counted in accordance with the activation function:
 Because the sigmoid function is used:
Because the sigmoid function is used:
 then sends a signal to all units on it (output units).
then sends a signal to all units on it (output units).
6. Each unit of output (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m), summed the weighted factors :
 Calculating according to the activation function :
Calculating according to the activation function :

7. Each unit of output (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m) receives a target pattern in accordance with the input pattern during training and calculate error : because f'(Y_ink) = Yk by using the sigmoid function, then :
because f'(Y_ink) = Yk by using the sigmoid function, then :

 Calculating the weight factor correction (to correct Wjk)
Calculating the weight factor correction (to correct Wjk)
 Calculating the correction correction :
Calculating the correction correction :
 and deliver value to the unit k layer beneath.
and deliver value to the unit k layer beneath.
8. Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ..., p), summing the delta inputs (from units in the upper layer)
 then multiplied by the activation function to compute the error.
then multiplied by the activation function to compute the error.
 Then calculate the weight correction (used to improve Vij)
Then calculate the weight correction (used to improve Vij)
 then calculate the bias correction (to correct Voj)
then calculate the bias correction (to correct Voj)
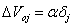
9. Each output unit (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., p)
 Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ... p) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., n)
Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ... p) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., n)

Backpropagation algorithm consists of two processes, namely the feed forward and backpropagation of error. To more clearly be described as follows :
1. Initialize weight factors with small random values.
2. Repeat steps 2 through 9 until the stop condition is met.
3. Perform steps 3 through 8 for each pair of training.
4. Each input unit (Xi, i = 1, ... n) receives input signals Xi and the signals are distributed to the upper unit of the hidden layer (hidden units).
5. Each hidden summing weighted factors :
 and counted in accordance with the activation function:
and counted in accordance with the activation function:
 Because the sigmoid function is used:
Because the sigmoid function is used:
 then sends a signal to all units on it (output units).
then sends a signal to all units on it (output units).
6. Each unit of output (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m), summed the weighted factors :
 Calculating according to the activation function :
Calculating according to the activation function :

7. Each unit of output (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m) receives a target pattern in accordance with the input pattern during training and calculate error :
 because f'(Y_ink) = Yk by using the sigmoid function, then :
because f'(Y_ink) = Yk by using the sigmoid function, then :

 Calculating the weight factor correction (to correct Wjk)
Calculating the weight factor correction (to correct Wjk)
 Calculating the correction correction :
Calculating the correction correction :
 and deliver value to the unit k layer beneath.
and deliver value to the unit k layer beneath.
8. Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ..., p), summing the delta inputs (from units in the upper layer)
 then multiplied by the activation function to compute the error.
then multiplied by the activation function to compute the error.
 Then calculate the weight correction (used to improve Vij)
Then calculate the weight correction (used to improve Vij)
 then calculate the bias correction (to correct Voj)
then calculate the bias correction (to correct Voj)
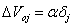
9. Each output unit (Yk, k = 1,2,3, ..., m) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., p)
 Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ... p) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., n)
Each hidden unit (Zj, j = 1,2,3, ... p) fixed bias and weight for (j = 0,1,2, ..., n)

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
